Arsenic contamination of groundwater is a major challenge causing serious arsenic poisoning to large numbers of people. There are several ways to remove arsenic from the ground water in order to make suitable for human consumption. However, arsenic contaminated sludge after treatment followed by filtration is discharged in land creating serious contamination of surface water. Similarly, toxic effects of tannery solid waste (TSW) and effluent on plants, animals and human are mainly reported with chromium toxicity. Hexavalent chromium is a powerful agent that induces mutations and causes cancer in animals and human. The effluents and sludge from tanning operations as well as from biological treatments are discharged into water bodies and onto land creating serious pollution problems. Electrical and electronic waste (e-waste) also accounts for one of the largest growing waste stream. E-wastes contain over 1000 different substances many of which are toxic and potentially hazardous for environment and human health. Although the metals like cu, Ag, Au are recovered, glass part of E-waste is most often dumped into landfills. Over time, the e-waste leads to certain amount of chemical and metal leaching. This can very often lead to ground water contamination.
CSIR-CGCRI investigated feasibility of utilization of all the above waste in glass making. Preliminary study has been undertaken and encouraging result obtained with the incorporation of As contaminated sludge obtained from water filtration, e-waste glass and tannery solid waste into glass matrix to develop various glass products. Incorporation of TSW into glass matrix may be used to produce filter glass particularly green filter glass and decorative glass article. Optimization of composition yield UV transmittance 70 % at ~370 nm and no significant visible transmission is recorded up to 750 nm. Similarly, As containing sludge is also incorporated into glass matrix and brown color glass is obtained. Significant chemical durability has also been observed in both the cases under submerged in distilled water at 75oC. No leaching of hazardous element (As, Cr, Fe, Co, Ni, Pb etc.) is detected in distilled water from the glass. The potential use of the glass containing As sludge can be in window panel significantly reducing electricity load in the building. The glass containing TSW can be used for development of different glass product such as green filter glass, decorated glass, table ware glass etc. In another study, 90% of e-waste glass can be reutilized as culet or raw material in glass making and various glass products glass particularly color glasses could be produced.
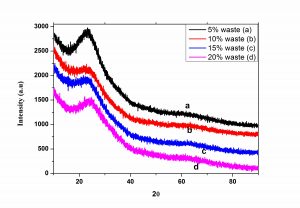
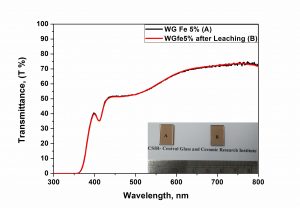
XRD profile of glass containing 5-20 wt.% of As contaminated sludge obtained from filtration of contaminated ground water; (Right) UV-Vis spectra of glass prepared with 5% As sludge before and after leaching study. (Inset: A – Polished Glass prepared with 5% As sludge; B-Glass after submerged in water for 14 days at 75oC).

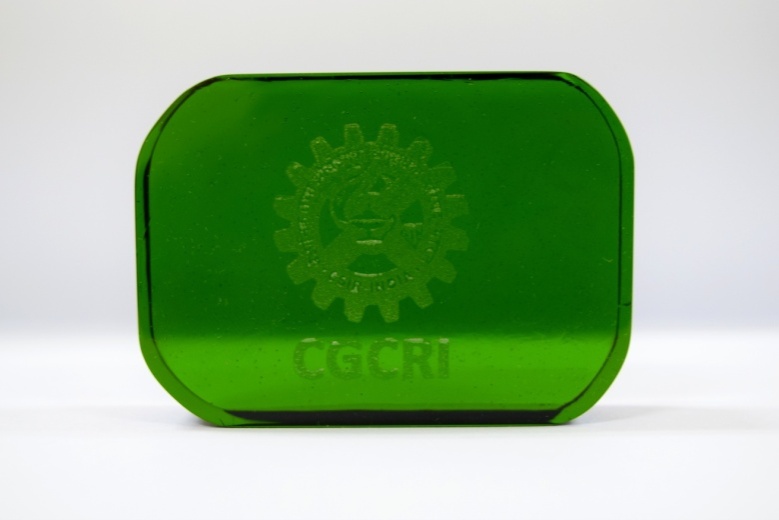
Glass souvenir prepared from Tannery solid waste

Blue colored glass utilizing tube light/fluorescent glass waste
Last Updated on January 28, 2021



